Which Figure Depicts An Animal Cell Placed In A Solution
5.four: Plasma Membrane
- Folio ID
- 16742
This simple, cutting-away model of an animal jail cell (Figure \(\PageIndex{i}\)) shows that a cell resembles a plastic handbag full of Jell-O. Its basic construction is a plasma membrane filled with cytoplasm. Like Jell-O containing mixed fruit, the cytoplasm of the jail cell also contains various structures, such equally a nucleus and other organelles. Your body is fabricated upwardly of trillions of cells, simply all of them perform the same bones life functions. They all obtain and use energy, respond to the environment, and reproduce. How do your cells conduct out these bones functions and keep themselves — and you — alive? To answer these questions, you need to know more nearly the structures that make up cells, starting with the plasma membrane.

The plasma membrane is a construction that forms a bulwark between the cytoplasm inside the cell and the environment exterior the jail cell. Without the plasma membrane, there would exist no prison cell. The membrane too protects and supports the cell and controls everything that enters and leaves it. It allows merely certain substances to pass through while keeping others in or out. To sympathize how the plasma membrane controls what passes into or out of the cell, you need to know its basic structure.
Phospholipid Bilayer
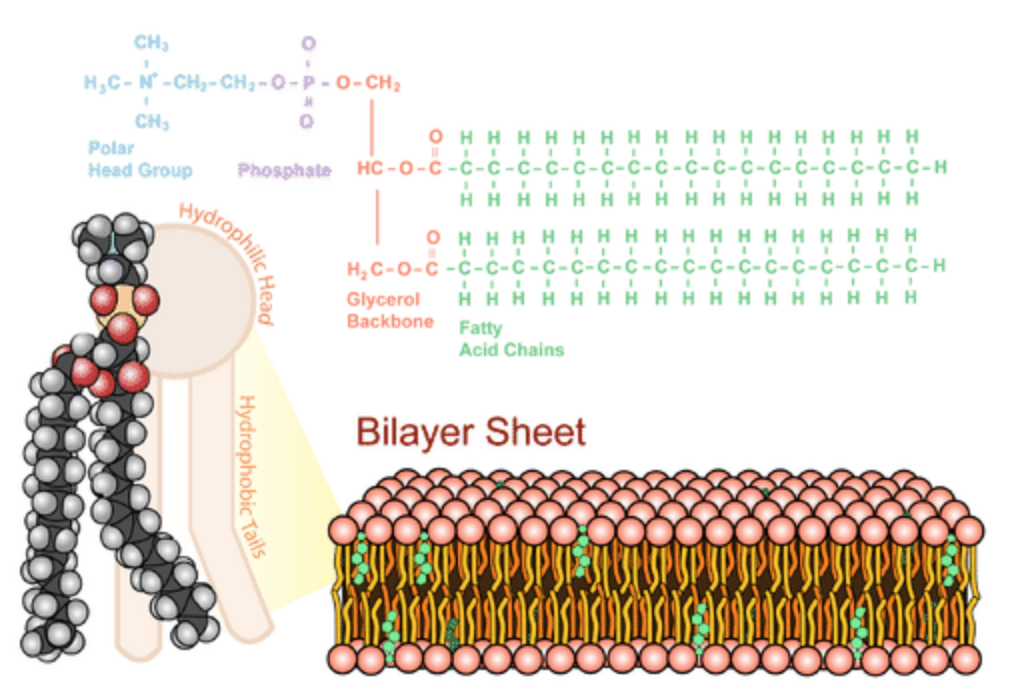
The plasma membrane is composed mainly of phospholipids, which consist of fatty acids and alcohol. The phospholipids in the plasma membrane are arranged in two layers, called a phospholipid bilayer, with a hydrophobic, or h2o-hating, interior and a hydrophilic, or h2o-loving, exterior. Each phospholipid molecule has a head and two tails. The caput "loves" water (hydrophilic) and the tails "fright" water (hydrophobic). The water-fearing tails are on the interior of the membrane, whereas the water-loving heads point outwards, toward either the cytoplasm or the fluid that surrounds the cell. The polar head group and fatty acrid chains are attached past a 3-carbon glycerol unit. Figure \(\PageIndex{two}\) shows a single phospholipid next to a phospholipid bilayer.
Molecules that are hydrophobic can easily pass through the plasma membrane if they are small enough because they are water-antisocial like the interior of the membrane. Molecules that are hydrophilic, on the other hand, cannot pass through the plasma membrane — at to the lowest degree non without help — considering they are h2o-loving like the exterior of the membrane.
Other Molecules in the Plasma Membrane
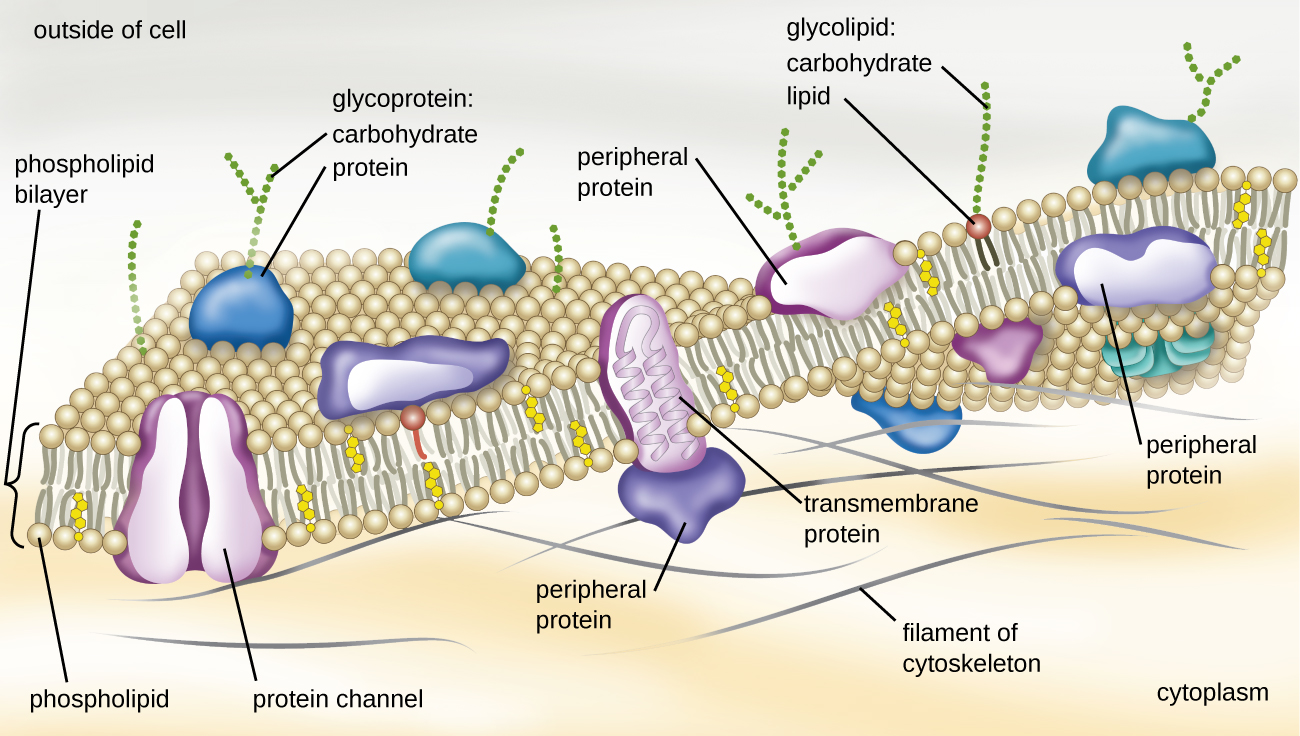
The plasma membrane also contains other molecules, primarily other lipids and proteins. The green molecules in Figure \(\PageIndex{ii}\), for example, are the lipid cholesterol. Molecules of the steroid lipid cholesterol help the plasma membrane go along its shape. (Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)) shows the cholesterol molecules as yellow structures within the middle of the phospholipid bilayer. Other structures shown in (Figure \(\PageIndex{3}\)):
- Poly peptide channels. These span the full membrane and have a space inside them because they are used to ship materials into or out of the cell.
- Transmembrane proteins. The root "trans" explains that these span (go "across") the membrane. Transmembrane proteins tin accept a diversity of functions.
- Peripheral proteins. These are plant only on one side of the membrane. They can be found on either the cytoplasmic side or the exterior of the membrane.
- Glycoproteins. These consist of a protein in the plasma membrane with chains of carbohydrates projecting out of the jail cell.
- Glycolipids. These are bondage of carbohydrates attached directly to a lipid in the membrane. Both glycoproteins and glycolipids deed equally labels to identify the cell.
- Filaments of cytoskeleton are found along the cytoplasmic side of the membrane and provide a scaffolding for the membrane.
Additional Functions of the Plasma Membrane
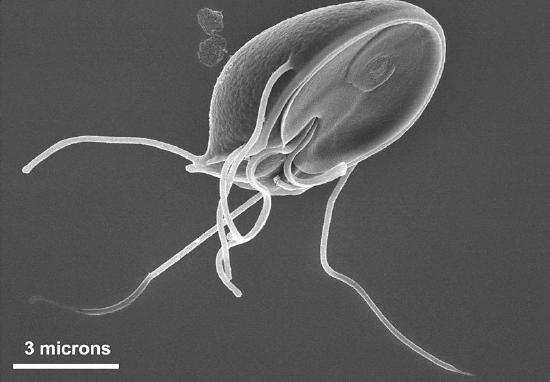
The plasma membrane may have extensions, such every bit whip-like flagella or brush-like cilia, that requite it other functions. In single-celled organisms, like those shown beneath, these membrane extensions may help the organisms move. In multicellular organisms, the extensions have different functions. For example, the cilia on human lung cells sweep strange particles and mucus toward the mouth and nose.
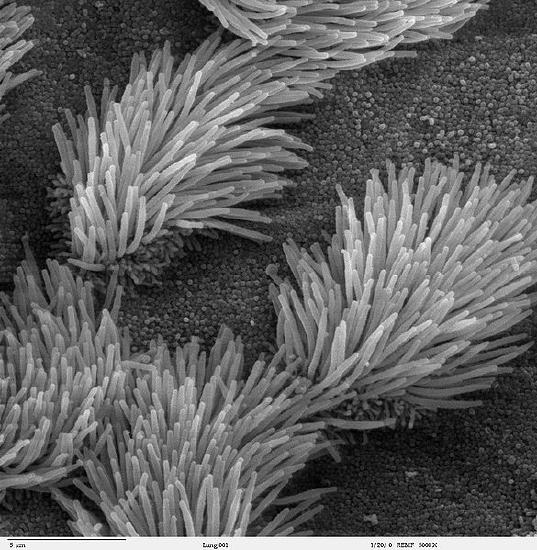

If yous smoke and need another reason to quit, here's a skillful one. Nosotros usually think of lung cancer as a major affliction caused by smoking. Just smoking tin can take devastating effects on the trunk's ability to protect itself from repeated, serious respiratory infections, such as bronchitis and pneumonia.
Cilia are microscopic, hair-like projects on cells that line the respiratory, reproductive, and digestive systems. Cilia in the respiratory system line most of your airways where they have the job of trapping and removing grit, germs, and other foreign particles before they can make you ill. Cilia secrete mucus that traps particles, and they move in a continuous moving ridge-like motion that sweeps the mucus and particles upward toward the throat, where they tin exist expelled from the body. When you are ill and cough upwardly phlegm, that'south what you lot are doing.
Smoking prevents cilia from performing these of import functions. Chemicals in tobacco smoke paralyze the cilia so they tin can't sweep fungus out of the airways and they also inhibit the cilia from producing mucus. Fortunately, these effects offset to habiliment off presently later the last exposure to tobacco fume. If you stop smoking, your cilia will return to normal. Fifty-fifty if prolonged smoking has destroyed cilia, they volition regrow and resume functioning in a thing of months after yous stop smoking.
Review
- What are the general functions of the plasma membrane?
- Depict the phospholipid bilayer of the plasma membrane.
- Identify other molecules in the plasma membrane, and land their functions.
- Why do some cells have plasma membrane extensions such as flagella and cilia?
- Explicate why hydrophilic molecules cannot hands pass through the jail cell membrane. What type of molecule in the prison cell membrane might help hydrophilic molecules pass through information technology?
- Which role of a phospholipid molecule in the plasma membrane is fabricated of fatty acid chains? Is this part hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
- The 2 layers of phospholipids in the plasma membrane are called a phospholipid ____________.
- True or False. The flagella on your lung cells sweep foreign particles and mucus toward your oral cavity and olfactory organ.
- Truthful or Simulated. Small hydrophobic molecules can hands laissez passer through the plasma membrane.
- True or Fake. The side of the cell membrane that faces the cytoplasm is hydrophilic.
- Steroid hormones can pass directly through cell membranes. Why exercise you think this is the instance?
- Some antibiotics work by making holes in the plasma membrane of bacterial cells. How do you lot think this kills the cells?
- What is the name of the long, whip-similar extensions of the plasma membrane that helps some single-celled organisms move?
Explore More than
- Animal prison cell model by Kevin Song, dedicated CC0 via Wikimedia Eatables
- Phospholipid bilayer by LadyofHats, CC Past-NC 3.0 for CK-12 Foundation
- Plasma membrane by CNX OpenStax, licensed CC BY 4.0 via Wikimedia Commons
- Giardia by CDC/ Dr. Stan Erlandsen, public domain via Wikimedia Eatables
- Bronchial cells by Charles Daghlian, released into the public domain via Wikimedia Commons
- Text adapted from Human Biology by CK-12 licensed CC By-NC 3.0
Source: https://bio.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Human_Biology/Book:_Human_Biology_%28Wakim_and_Grewal%29/05:_Cells/5.04:_Plasma_Membrane
Posted by: boozeyoring40.blogspot.com

0 Response to "Which Figure Depicts An Animal Cell Placed In A Solution"
Post a Comment